-
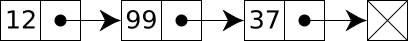
A linked list consists of a sequence of objects known as nodes.
-
Each node contains
-
arbitrary data fields;
-
link pointing to the next node;
-
(optional) link pointing to the previous node.
-
-
For example, a singly-linked list contains two values:
-
the value of the current node
-
link to the next node:
struct Node { int data; Node* pnext; };
-