-
// Node.h class Node { Node* pnext; public: int data; // Remove node in front: void remove_next() { if ( pnext == NULL ) return; Node* obsolete = pnext; this->pnext = obsolete->pnext; // Make node "single": obsolete->pnext = NULL; } };The following diagram shows how it works:

-
To remove the node, program must again keep track of the previous node:
#include "Node.h" int main ( ) { Node A; Node B; Node C; A.data = 12; B.data = 99; C.data = 37; A.insert( &C ); A.insert( &B );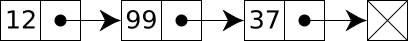
A.remove_next();

return 0; }