-
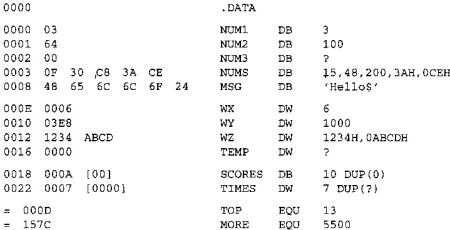
Representing data types in assembly source files requires appropriate assembler directives.
-
The directives allocate data and format x86 little-endian values.
-
Bytes are allocated by define bytes DB.
-
Words are allocated by define words DW.
-
Both allow more than one byte or word to be allocated.
-
Question marks specify uninitialized data.
-
Strings allocate multiple bytes.
-
Labels in front of the directives remember offsets from the beginning of the segment which accommodates the directive.
-
DUP allows to allocate multiple bytes. The following two lines produce identical results:
DB ?, ?, ?, ?, ? DB 5 DUP(?) -
Note that EQU directive does not allocate any memory: it creates a constant value to be used by Assembler:
CR EQU 13 DB CR . mov al, CR