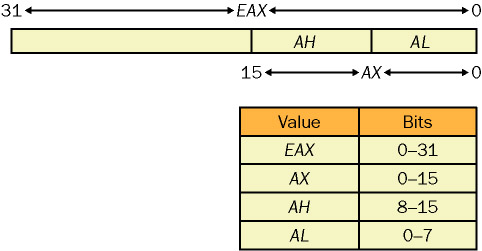
-
Register operands refer to data stored in registers. The following examples show typical register operands:
mov bx, 10 ; Load constant to BX add ax, bx ; Add BX to AX jmp di ; Jump to the address in DI -
An offset stored in a base or index register often serves as a pointer into memory.
-
You can store an offset in one of the base or index registers, then use the register as an indirect memory operand. For example:
mov [bx], dl ; Store DL in indirect memory operand inc bx ; Increment register operand mov [bx], dl ; Store DL in new indirect memory operand -
This example moves the value in DL twice to 2 consecutive bytes of a memory location pointed to by BX.
-
Example shows that changing BX register causes it to point to a different location in memory.