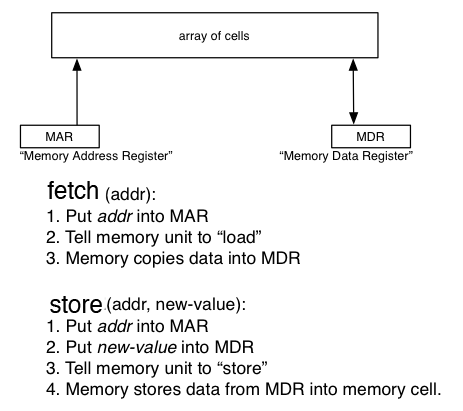
-
There are two key operations on memory:
-
fetch( address ) returns value without changing the value stored at that address.
-
store( address, value ) writes new value into the cell at the given address.
-
-
This type of memory is random-access, meaning that CPU can access any value of the array at any time (vs. sequential access, like on a tape).
-
Such memories are called RAM (random-access memory.)
-
Some memory is non-volatile, or read-only (ROM or read-only memory.)
-
Memory Operations: