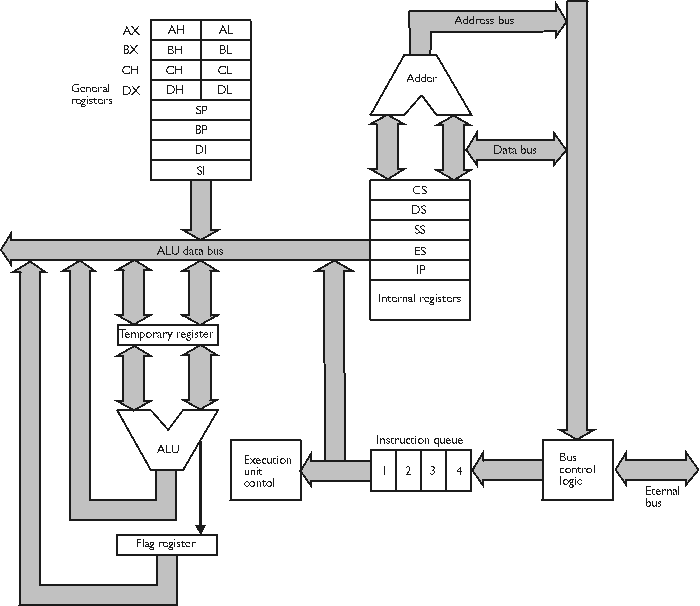
-
Year 1979
-
The 8088, 8086, and 80286 are 16-bit CPUs.
-
Internal registers are 16 bits in size.
-
The 8086 is faster than the 8088 because of its 16-bit data bus; the 8088 has only an 8-bit data bus.
-
The 16-bit data bus allows you to use EVEN and ALIGN on an 8086 processor to word-align data and thus improve data-handling efficiency.
-
Memory addresses on the 8086 and 8088 refer to actual physical addresses.
-
The 8086 and 8088 have 20 address pins, and 1 megabyte of addressable memory (which is the real mode segmented memory explained later) requires addresses of 20 bits in size.
-
See also: