3-606
INSTRUCTION SET REFERENCE
REP/REPE/REPZ/REPNE
/REPNZRepeat String Operation Prefix
(Continued)
The REP prefixes apply only to one string instruction at a time. To repeat a block of instructions,
use the LOOP instruction or another looping construct.
All of these repeat prefixes cause the associated instruction to be repeated until the count in
register (E)CX is decremented to 0 (refer to the following table). If the current address-size
attribute is 32, register ECX is used as a counter, and if the address-size attribute is 16, the CX
register is used. The REPE, REPNE, REPZ, and REPNZ prefixes also check the state of the ZF
flag after each iteration and terminate the repeat loop if the ZF flag is not in the specified state.
When both termination conditions are tested, the cause of a repeat termination can be deter-
mined either by testing the (E)CX register with a JECXZ instruction or by testing the ZF flag
with a JZ, JNZ, and JNE instruction.
When the REPE/REPZ and REPNE/REPNZ prefixes are used, the ZF flag does not require
initialization because both the CMPS and SCAS instructions affect the ZF flag according to the
results of the comparisons they make.
A repeating string operation can be suspended by an exception or interrupt. When this happens,
the state of the registers is preserved to allow the string operation to be resumed upon a return
from the exception or interrupt handler. The source and destination registers point to the next
string elements to be operated on, the EIP register points to the string instruction, and the ECX
register has the value it held following the last successful iteration of the instruction. This mech-
anism allows long string operations to proceed without affecting the interrupt response time of
the system.
When a fault occurs during the execution of a CMPS or SCAS instruction that is prefixed with
REPE or REPNE, the EFLAGS value is restored to the state prior to the execution of the instruc-
tion. Since the SCAS and CMPS instructions do not use EFLAGS as an input, the processor can
resume the instruction after the page fault handler.
Use the REP INS and REP OUTS instructions with caution. Not all I/O ports can handle the rate
at which these instructions execute.
A REP STOS instruction is the fastest way to initialize a large block of memory.
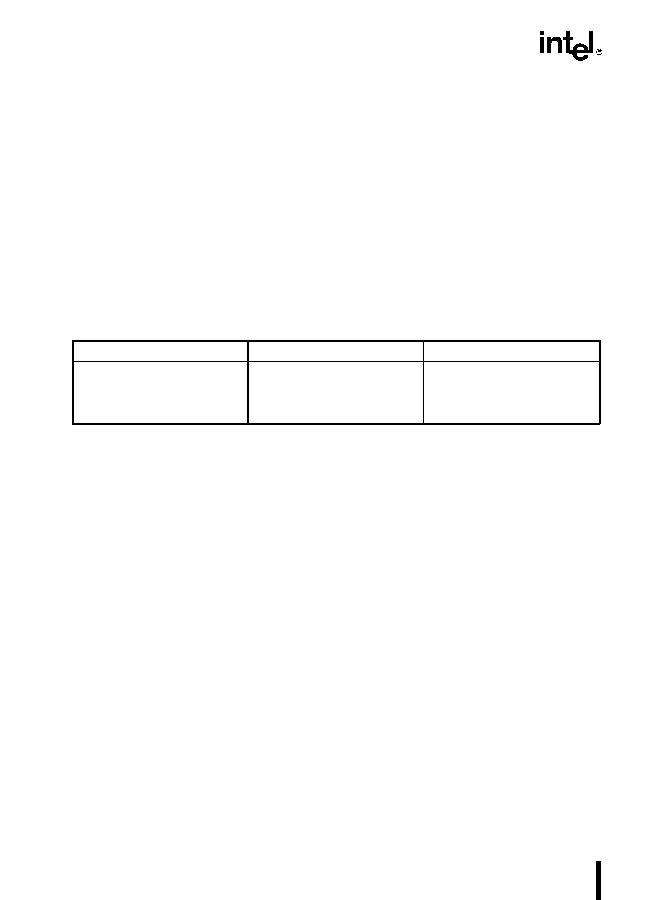
Repeat Conditions
Repeat Prefix
Termination Condition 1
Termination Condition 2
REP
ECX=0
None
REPE/REPZ
ECX=0
ZF=0
REPNE/REPNZ
ECX=0
ZF=1