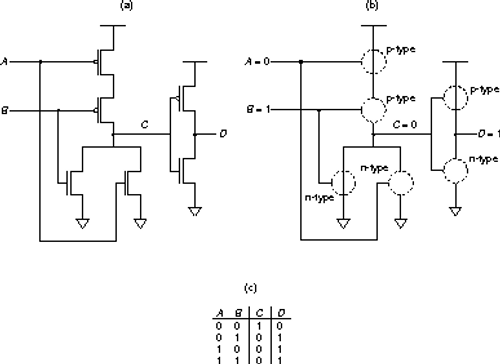
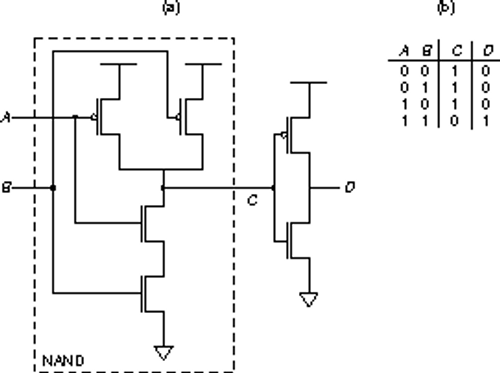
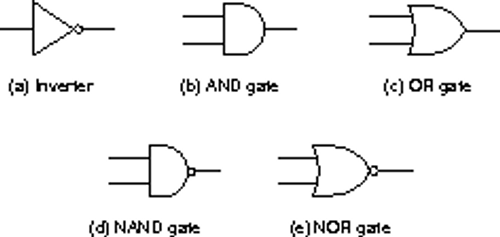
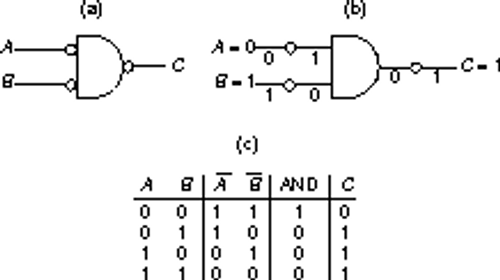
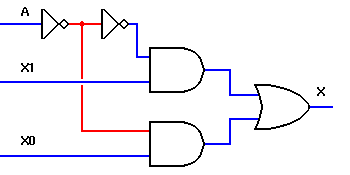
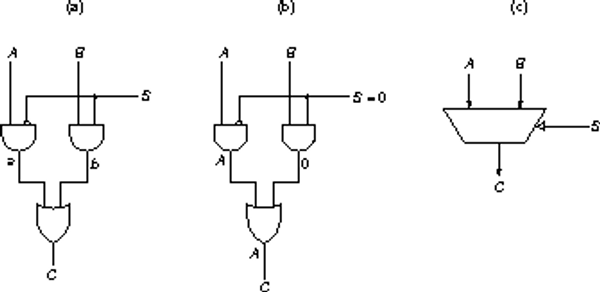
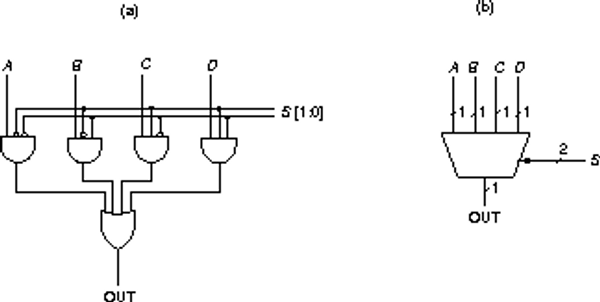
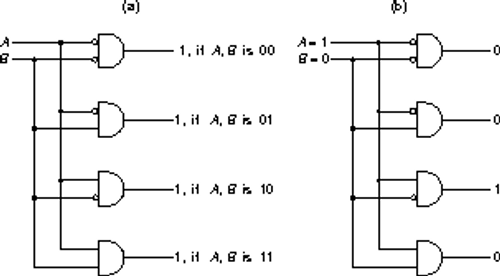
-
BJT stands for bipolar junction transistor.
-
BJT transistors are used primarily in amplifying or switching applications (e.g. power supplies.)
-
FET stands for the field-effect transistor.
-
FET transistors rely on an electric field to control conductivity of a channel.
-
JFET stands for the junction gate field-effect transistor (or JUGFET), and is the simplest type of the field effect transistor.
-
See also: wikipedia articles about transistors and JFET transistors.
-
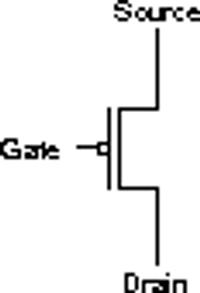
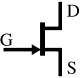
Common transistor circuit symbols:
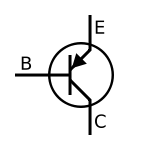
PNP 
P-channel 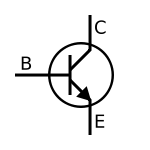
NPN 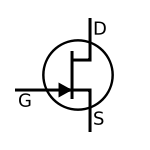
N-channel BJT JFET