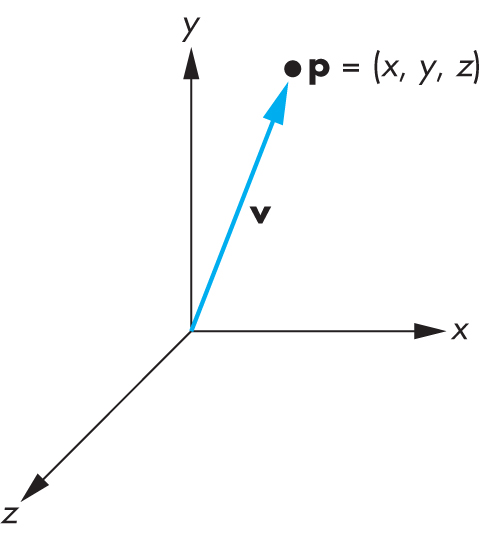
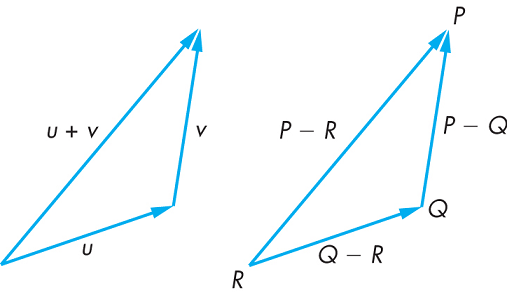
-
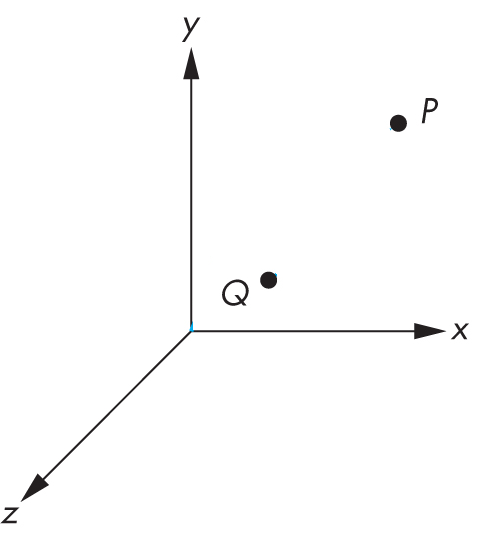
Points in 3D space, such as P and Q
- specify location in space
- don't have size or shape
Course list http://www.c-jump.com/bcc/
|

|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|

|
The following properties of dot product make it especially important for us:
If u and v are of unit length (the length of 1), then u·v is the cos(a)
The dot product is used extensively during diffuse lighting calculations. It is taken between a surface normal and the vector pointing toward a light source. When the angle is zero, the light intensity is at its maximum.
The magnitude (length) of a vector is usually measured as
|v| = sqrt( v·v )
If
u·v = 0
then u and v are orthogonal (positioned at 90 degree angle)
|
|
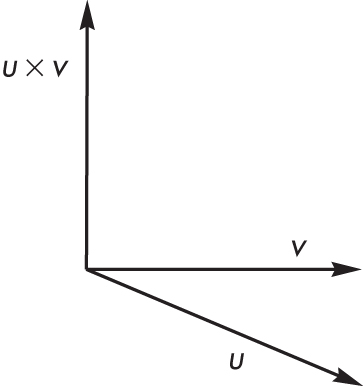
Note: unlike the dot product, the order of vectors is important: if the order is reversed, the reseulting vector is pointing in the opposite direction:
u×v = N
v×u = -N
The cross product gives a consistent orientation: given the usual x and y axis in space, the u×v is pointing in the direction of the positive z axis.
The cross product has numerous purposes, including finding normals and constructing translation matrices.
|

|
|

|