-
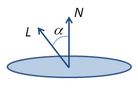
If vectors L and N are normalised, cos(a) is the dot product:
-
cos(a) = L·N
-
-
The diffuse intensity Id is computed by adding the diffuse component of the object's material, Kd:
-
Id = Kd * L·N
-
-
In practice, we need to avoid negative L·N values:
-
Id = Kd * max( L·N, 0 )
-
-
Also, we can now easily add ambient light Ia to the result:
-
Id = max(
Kd * max( L·N, 0 ),
Ia
)
-
-
where Ia is the ambient light intensity.
-
-
L – the incoming light vector
-
N – the normal of the plane/vertex