
Course list http://www.c-jump.com/bcc/
New Technology File System, NTFS -- latest Windows file system.
Supports:
Large volume storage solution
High performance
System facility that repairs itself
Advanced file-level features:
security
compression
auditing.
Uses self-recovering disks.
See also
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NTFS
Data security -- the capability to encrypt/decrypt files/folders.
16-bit Unicode -- character set to name files and folders allows multiligual support for native languages for users around the world.
Fault tolerance -- modifications recorded in a special log file - the $LogFile:
If system crashes, NTFS examines the $LogFile and restores the disk to a consistent state with minimal data loss.
All data in NTFS file system is allocated to a file.
The the first few sectors of the volume contain the boot sector and boot code.
Any sector beyond those can be allocated to a file.
No dependence on underlying hardware:
NTFS expects in new disk technologies that 512-byte sector isn't the only option
The cluster size can be specified when formatting the volume
NOTE: File compression features are not available if the cluster size is greater than 4KB.
Volume size default cluster size
512MB-1GB -- 1KB
1-2GB -- 2KB
2GB+ -- 4KB
No limit on file size
Native support for encryption, compression, recoverability
Flexible permissions on each file
NTFS maintains a transaction log and change journal
in the event of a failure NTFS automatically restores the consistency of the file system.
NTFS can natively compress and encrypt files without the use of a separate application.
The file is
encrypted/compressed during the file write, and
decrypted/uncompressed during the file read operation
Compression/Encryption is transparent to user.
File permissions track users and groups and can prevent unauthorized access to a file.
Additional time stamps and hard links were added.
In order to gain POSIX compliance, case sEnSiTiVe file names are used:
FAT saved everything in uppercase
HPFS, while it did save the case of a file's name, referred to the same file no matter how you mixed the case when opening it
Under NTFS
README.TXT
Readme.txt
readme.txt
are all different files.
Maximum cluster size is 64 KB
File names are limited to 255 UTF-16 characters
MBR disks only support partition sizes up to 2 TB
GPT volumes must be used to create NTFS volumes over 2 TB
NOTE: GPT partitions require 64-bit platform
Presently, maximum NTFS file size is roughly 16 TB
FAT12 - 12 bit allocation system used on floppy diskettes.
Windows 2000 will default to formatting a very small volume (64MB flash card, for instance) with FAT12 to prevent waste of space for the overhead incurred with other file systems.
Every operating system uses FAT12 for floppies to allow for interoperability.
FAT16 - 16-bit allocation used on small (less than 2GB) hard drives.
Was sufficient for small volumes on personal computers, but lacked the performance and stability needed for a file server.
The 8.3 file naming convention was a serious limitation that tormented users for years.
FAT32 - uses 32-bit allocation table to overcome size limitations on the 16-bit system.
Above 500 MB, FAT16 required cluster sizes that started to induce large amounts of wasted slack space and performance lagged.
Introduced with Windows 95 OSR2, mainstreamed with Windows 98.
Long filename support provided as a horrendous kludge in a sequence of directory entry structures.
HPFS - High Performance File System - built for speeed!
Designed as a joint venture between Microsoft and IBM and included many marked improvements over FAT.
Improvements included
long filename support,
512-byte allocation units (which almost completely did away with file slack),
The 386 version had nothing to do with CPU architecture, but rather used the name as the latest marketing buzzword meaning 'faster'.
It had a larger file I/O cache and some other minor improvements that resulted in a marked performance boost for the server version of OS/2.
But, it was released about the same time IBM and MS split and IBM had to pay royalties to MS anytime it sold HPFS386 so it was not widely used.
Windows support for this FS dropped with Windows 2000.
See also
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_Performance_File_System
NTFS - while many consider it a new file system built from the ground up, it is largely based on HPFS.
NTFS incorporates all the features of HPFS and Macintosh's HFS and overcomes many performance and security issues they lacked.
Where HPFS performance starts degrading above 400 MB volumes, NTFS's performance theoretically doesn't drop off right up to the theoretical volume limit of 16-Exabyte (2TB is the practical limit, but remains to be seen when drives get that big become mainstream.)
More info regarding NTFS comparison with its predecessors:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_file_systems
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/100108
Format program for NTFS volume allocates first 16 sectors for the boot sector followed by bootstrap code.
The first sector of NTFS partition is the boot sector, or VBR, the volume boot record.
Contains file system type, size, and location of NTFS data.
Also contains boot code.
Also accessible by entry #7 in $MFT.
The boot sector is backed up at the end of the volume.
Offset/Purpose:
0-2 three bytes of Jump instruction (Assembly code) to jump to boot code (mandatory in bootable partition.)
3-10 OEM name in ASCII (OEM ID)
11-12 Bytes per sector (BPB)
13 Sectors per cluster
14-15 Reserved (Microsoft says to set this to 0)
16-20 Unused (Microsoft says to set this to 0)
21 Media descriptor
22-23 Unused (Microsoft says to set this to 0)
24-31 Unused (Microsoft says that this is not checked)
32-35 Unused (Microsoft says to set this to 0)
36-39 Unused (Microsoft says that this is not checked)
40-47 Total sectors in file system
48-55 Starting cluster address of $MFT
56-63 Starting cluster address of $MFT Mirror $DATA attribute
64 Size of MFT entry
65-67 Unused
68 Size of index record (directory entry)
69-71 Unused
72-79 Serial number
80-83 Unused
84-509 Bootstrap code
510-511 End of Sector Marker Signature (0xAA55 magic number)
MFT is a unique, database-like structured file, named the Master File Table, internally $MFT.
The MFT contains a record for every file and folder on NTFS volume.
First 16 entries in the MFT are reserved for NTFS metadata -- the system files.
File attributes, size, date/time stamps, and permissions are saved in MFT entries.
When number of files grows, the size of the MFT increases.
When a file is deleted, the $MFT entry is marked free (to be reused by a new file in the future.)

Everything in NTFS is a file.
The MFT is a file.
The boot sector is a file.
Directory entries are files that contain a list of other files.
NTFS was designed as a database. Microsoft's documentation says, "The MFT is a relational database that consists of rows of file records and columns of file attributes. It contains at least one entry for every file on an NTFS volume, including the MFT itself."
Each MFT record is 1K (1024 bytes) long.
The only weakness of MFT aproach that it can grow to a very large size.
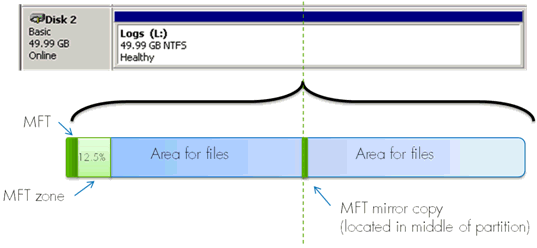
The MFT Zone is a chunk of free space immediately following the $MFT.
MFT Zone is reserved for potential MFT growth.
Once free space in the original $MFT file is used up, the MFT Zone is divided in half.
New file records are created in the bottom half (not near the original $MFT.)
If the entire MFT Zone is used up and the MFT still has to grow, then the $MFT file becomes fragmented.
A fragmented $MFT file cannot be defragmented.
MFT Sys File Rec Name Description --- ---------- --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0 $MFT.......MFT 1: file records on NTFS volume - an indef of every file. 1 $MftMirr...MFT 2: a backup of first 4 records of $MFT for recovery purposes. 2 $LogFile...Log File: the transaction log of recent file transactions for recovery purposes. 3 $Volume....Volume: volume information table - serial number, creation time, dirty flag. 4 $AttrDef...Attribute definitions: list of file attribute definitions. 5 "." .......Root folder: volume root folder (named ".") 6 $Bitmap....Bitmap: maps the availability (free/in-use) of the volume clusters. 7 $Boot......VBR, the Boot sector: used to mount the NTFS volume during the bootstrap process. 8 $BadClus...Bad cluster file: map of clusters with unrecoverable I/O errors. 9 $Secure....On Windows 2000 - Security file: the access control list with unique security descriptors for files. 9 $Quota.....Quota Information - the amount of space allowed for each user 10 $UpCase....Upcase table: table to convert uppercase characters to lowercase Unicode characters for collating. 11 $Extend....On Windows 2000 - NTFS extension file: Optional extensions like quotes and object identifiers. 12-15..........Unused, but marked "in use" 16-23..........Unused, but marked "unused" Any.$Reparse...Reparse point information Any.$UsnJrnl...Journaling of Encryption s
NOTE: the record number of the MFT entry is often called the inode.
The system files remain hidden from the user on NTFS volume.
They describe various pieces of the file system.
The MFT will always have at least 16 records, which are reserved for the system files.
The system files are records 0-11.
MFT records 12-15 are marked "in use", but are empty (reserved for future use.)
MFT records 16-23 are marked "not in use," but are never used.
Each $MFT entry (record) is 1,024 (0x400) bytes in length
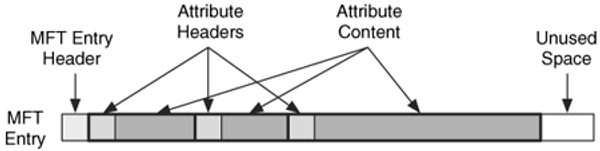
Each MFT entry starts with a 42-byte sized header
Small files may be fully contained within an MFT records
Offset/Purpose
0-3 Signature: ether FILE or BAAD, which denotes a bad entry.
4-5 Offset to fixup array
6-7 Number of entries in fixup array
8-15 $LogFile sequence number
16-17 Sequence value
18-19 Link count
20-21 Offset to first attribute
22-23 Flags:
0x00 not in use
0x01 in use
0x02 directory
0x03 directory in use
Deleting a file changes the flag to 0x00, but does nothing to clear out the data, thus many deleted file's metadata is still recoverable as long as the record hasn't been recycled.
24-27 Used size of MFT entry
28-31 Allocated size of MFT entry
32-39 File reference to base record
40-41 Next attribute identifier
42-1,023 Attributes and fixup values

Difference between NTFS 3.1 and previous NTFS versions is the inclusion of the record number at offset 0x2C. Due to this change, the byte after the word 'FILE' changes the ASCII letter from asterisk "*" to zero "0".
After the header, the remainder of the MFT entry contains attributes about the file.
All attributes have a header and data stream (i.e., contents.)
Resident attribute contents stored in the MFT entry with the header:
stored within the MFT without the need for additional storage.
Non-resident attribute contents stored in external clusters.
A cluster run entry identifies the external clusters.
Type -- Attribute -- Name -- Purpose 0x10 16....$STANDARD_INFORMATION --- General information --- flags, MAC times, owner, and security id. 0x20 32....$ATTRIBUTE_LIST --- Pointers to other attributes and a list of nonresident attributes. 0x30 48....$FILE_NAME --- File name --- (Unicode) and outdated MAC times 0x40 64....$VOLUME_VERSION --- Volume information --- NTFS v1.2 only and Windows NT, no longer used 0x40 64....$OBJECT_ID --- 16B unique identifier --- for file or directory (NTFS 3.0+; Windows 2000+) 0x50 80....$SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR --- File's access control list and security properties 0x60 96....$VOLUME_NAME --- Volume name 0x70 112...$VOLUME_INFORMATION --- File system version and other information 0x80 128...$DATA --- File contents 0x90 144...$INDEX_ROOT --- Root node of an index tree 0xA0 160...$INDEX_ALLOCATION --- Nodes of an index tree --- with a root in $INDEX_ROOT 0xB0 176...$BITMAP --- Bitmap --- for the $MFT file and for indexes (directories) 0xC0 192...$SYMBOLIC_LINK --- Soft link information --- (NTFS v1.2 only and Windows NT) 0xC0 192...$REPARSE_POINT --- Data about a reparse point --- used for a soft link (NTFS 3.0+; Windows 2000+) 0xD0 208...$EA_INFORMATION --- Used for backward compatibility with OS/2 applications (HPFS) 0xE0 224...$EA --- Used for backward compatibility with OS/2 applications (HPFS) 0x100 256..$LOGGED_UTILITY_STREAM --- Keys and other information about encrypted attributes (NTFS 3.0+; Windows 2000+)
To allow basic file I/O, any file will have:
$STANDARD_INFORMATION
$FILE_NAME (two will exist if 8.3 name creation is turned on)
$DATA
Similarly, a directory will have:
$STANDARD_INFORMATION
$FILE_NAME (two will exist if 8.3 name creation is turned on)
$INDEX_ROOT
$INDEX_ALLOCATION
Every MFT entry, file or directory, must have a $STANDARD_INFORMATION and at least one $FILE_NAME.
If the file name has more than 8 characters, there is a second $FILE_NAME attribute.
If file is empty, it will have the $DATA attribute with nothing in it.
Likewise, if directory is empty, it will have two index attributes
Any standard NTFS attribute has a header:
length, because attributes have variable lengths
optional name
flags
how to find it on disk (if the attribute resides elsewhere on disk -- not inside the MFT record)
etc.
Attributes can be one of the following four types:
Resident and Named
Resident and Unnamed
Non-Resident and Named
Non-Resident and Unnamed
Offset Size Value Description ------ ---- ----- -------------------------------- 0x00 4 Attribute Type (e.g. 0x10, 0x60) 0x04 4 Length (including this header) 0x08 1 0x00 Non-resident flag 0x09 1 0x00 Name length 0x0A 2 0x00 Offset to the Name 0x0C 2 0x00 Flags 0x0E 2 Attribute Id (a) 0x10 4 L Length of the Attribute 0x14 2 0x18 Offset to the Attribute 0x16 1 Indexed flag 0x17 1 0x00 Padding 0x18 L The Attribute data (a) Each attribute has a unique identifier
Byte Offset Size Value Description ------ ---- ----- -------------------------------- 0x00 4 Attribute Type (e.g. 0x90, 0xB0) 0x04 4 Length (including this header) 0x08 1 0x00 Non-resident flag 0x09 1 N Name length 0x0A 2 0x18 Offset to the Name 0x0C 2 0x00 Flags 0x0E 2 Attribute Id (a) 0x10 4 L Length of the Attribute 0x14 2 2N+0x18 Offset to the Attribute (b) 0x16 1 Indexed flag 0x17 1 0x00 Padding 0x18 2N Unicode The Attribute's Name 2N+0x18 L The Attribute (c) (a) Resident attributes cannot be compressed (b) Each attribute has a unique identifier (c) Rounded up to a multiple of 4 bytes
Byte Byte Offset Size Value Description ------ ---- ----- -------------------------------- 0x00 4 Attribute Type (e.g. 0x20, 0x80) 0x04 4 Length (including this header) 0x08 1 0x01 Non-resident flag 0x09 1 0x00 Name length 0x0A 2 0x00 Offset to the Name 0x0C 2 Flags 0x0E 2 Attribute Id (a) 0x10 8 Starting VCN 0x18 8 Last VCN 0x20 2 0x40 Offset to the Data Runs 0x22 2 Compression Unit Size (b) 0x24 4 0x00 Padding 0x28 8 Allocated size of the attribute (c) 0x30 8 Real size of the attribute 0x38 8 Initialized data size of the stream (d) 0x40 ... Data Runs (a) Each attribute has a unique identifier (b) Compression unit size = 2x clusters. 0 implies uncompressed (c) This is the attribute size rounded up to the cluster size (d) Always equal to the allocated size?
Byte Byte Offset Size Value Description ------ ---- ----- -------------------------------- 0x00 4 Attribute Type (e.g. 0x80, 0xA0) 0x04 4 Length (including this header) 0x08 1 0x01 Non-resident flag 0x09 1 N Name length 0x0A 2 0x40 Offset to the Name 0x0C 2 Flags 0x0E 2 Attribute Id (a) 0x10 8 Starting VCN 0x18 8 Last VCN 0x20 2 2N+0x40 Offset to the Data Runs (b) 0x22 2 Compression Unit Size (c) 0x24 4 0x00 Padding 0x28 8 Allocated size of the attribute (d) 0x30 8 Real size of the attribute 0x38 8 Initialized data size of the stream (e) 0x40 2N Unicode The Attribute's Name 2N+0x40 ... Data Runs (b) (a) Each attribute has a unique identifier (b) Rounded up to a multiple of 4 bytes (c) Compression unit size = 2x clusters. 0 implies uncompressed (d) This is the attribute size rounded up to the cluster size (e) Always equal to the allocated size?
Type 0x10 -- a required, first attribute in every file.
Contains:
MAC timestamps
DOS file permissions
Tracking info for version, logging, quota, security --
Most of this extra info relates to optional functionality and is not normally turned on.
Flag Description ------ -------------------- 0x0001 Read-Only 0x0002 Hidden 0x0004 System 0x0020 Archive 0x0040 Device 0x0080 Normal 0x0100 Temporary 0x0200 Sparse File 0x0400 Reparse Point 0x0800 Compressed 0x1000 Offline 0x2000 Not Content Indexed 0x4000 Encrypted
MAC times are stored in a number of places in an NTFS file entry
$STANDARD_INFORMATION timestamps are kept current.
$FILE_NAME timestamps are outdated!
File access time is the last time that the file was accessed in any way and has a granularity of 1 hour.
(This prevents constant excessive update to the metadata.)
Windows converts
the MAC times from the local time to UTC time, and stores UTC time.
UTC time to local time for display
Interpretation problems occur if disk is examined on a system with a different time zone setting.
Type 0x20 -- if the are a lot of resident attributes and not enough space to fit them in the MFT record, they are moved into another MFT record. The $ATTRIBUTE_LIST specifies how to find these additional MFT records.
This is a quite rare attribute, a couple examples might be
A large file can be extremely fragmented, requiring very long runlist of data runs
A file has a lot of named streams
Type 0x30 -- contains
the inode number of the parent directory that contains this file. Parent Directory Reference has two parts:
6 bytes for the inode number of the parent, and
2 bytes for an internal sequence number for NTFS integrity checks
Timestamps are repeated -- the same as in $STANDARD_INFORMATION, but here the timestamps are often out of sync:
they are not updated unless the file name changes
only if the file is renamed, the times are also updated.
File size (file length)
both the actual size of the file, and
the amount of disk space allocated -- the actual size + cluster slack are recorded.
Flags -- the same as in $STANDARD_INFORMATION
The name of the file. After the name, the entry is padded with 0x00 to an even 8 byte cutoff point.
NOTE: If 8.3 file name creation is turned on, any files with long names will have a second $FILE_NAME attribute that contains the short name.
Type 0x40 -- specifies an ID that allows tracking the file in the event if its name or location changes.
Mostly use by Microsoft Office embedded documents (aka compound files.)
Every file that has $OBJECT_ID will have it registered in $ObjId system file.
Type 0x50 -- tracks the owner of the file and pemissions granted by that owner to everyone else.
The structure changes depending on how many and what type of Access Control Lists (ACL) are present on the file. Possible entries are:
Attribute header
Revision
Flags
Offset to user SID
Offset to group SID
Offset to SACL
Offset to DACL
DACL
user SID
group SID
Type 0x60 -- contains the volume name
Because drive letters such as C: or D: etc. aren't descriptive enough.
Allows NTFS volumes to have long names with special characters in different languages.
Prior to $VOLUME_NAME the only alternative was an "OEM label" located in the boot sector.
Type 0x70 -- contains info about the volume:
NTFS version number, e.g. 1.2 or 3.1 NTFS version
Flags:
Value Description ------ ------------------- 0x0001 Dirty 0x0002 Resize LogFile 0x0004 Upgrade on Mount 0x0008 Mounted on NT4 0x0010 Delete USN underway 0x0020 Repair Object Ids 0x8000 Modified by chkdsk
If the dirty flag is set, on the next reboot chkdsk /f will run.
Type 0x80 -- contains the actual file content -- user data
Can be any of the four possible attribute types:
Resident and Named
Resident and Unnamed (if the file is small enough to fit in MFT entry)
Non-Resident and Named
Non-Resident and Unnamed (most common)
A runlist is used to point to a set of clusters associated with a non-resident attribute of a file
Processing the runlists allows for the assembly of the file from the clusters comprising the contents.
Specifies
cluster offset
length of a run
Type 0x90 -- establishes top-level parameters for the index:
collation rules
entry size
length of entire index
Type 0xA0 -- describes components that make up the index:
storage containers for B-tree components
The $INDEX_ALLOCATION attribute is named to correlate with the $BITMAP attribute to a specific index, because some files with indexes can have multiple indexes.
Always a non-resident attribute. If index is small enough to fit in MFT entry, then $INDEX_ROOT is used instead.
Type 0xB0 -- used with $INDEX_ALLOCATION attributes and in $MFT entries
Contains string of bits that correlates to a set of records
Purpose: to show which entries are in use and which are free
Note that individual entries in $MFT have their own marking of free or in use, but bitmaps allow for quick view of the whole structure with multiple records.
This attribute is named so the bitmap is correlated to a specific index, since some files with indexes can have multiple indexes.
For example, a bitmap
0x7FFF =
0111111111111111 =
means that the first entry is not is use; next 15 are in use.
Type 0xC0(*) -- allows the $MFT entry to be re-processed in another way, if compared to a regular file.
When opening a file is taking place, it is processed in a "normal way." Then, if $REPARSE_POINT attribute is found, the file is "re-processed" as
symbolic link
volume mount point
remote storage service
__________________
(*) In NTFS version 1.x this attribute was named $SYMBOLIC_LINK, but later the functionality was broadened and now we have the $REPARSE_POINT.
A Symbolic Link is not the same as Hard Link. A Hard Linked file has two file names and editing either name updates the same data.
A Symbolic Link is a separate file that contains no data, only a pointer to the other file.
If a Symbolic Link file is opened for reading, the $REPARSE_POINT attribute is processed and the file system will open a different file specified there.
See also
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NTFS_symbolic_link
Reparsing is a very powerful feature of NTFS
The "reparsing" is very flexible and can be extended into almost any kind of action
There are several "canned" reparse point types, but a driver can be written to do anything and a file can be "reparsed" however that driver wants to "read" it.
This can allow the same data to be read different ways, depending on the variables sent to the driver.
Types 0xD0 and 0xE0 -- outdated.
They used to implementextended HPFS attributes on OS/2 and WinNT server.
Type 0x100 -- layout and treatment is similar to $DATA attribute
Every EFS encrypted file will have this attribute to store the file encryption key used during encryption/decryption
The purpose of this file is to backup the starting point of the $MFT.
$MFTMirr is usually located half way through the volume.
It only contains the vital records needed to get the $MFT readable again.
$MFTMirr is always either 4 records, or one cluster.
Generally, the record size in the MFT is 1024 bytes and the cluster size of the drive is 4048 bytes.
In 90% of cases the $MFTMirr will contain 4 MFT records.
In case of the cluster size being smaller than 4K, $MFTMirr occupies as many clusters as necessary to accommodate first 4 records of the MFT
If the cluster size is bigger than 4K, then there is more room, and it may contain more than 4 records.
(Since having clusters larger than 4K breaks some of the other features, such as compression, this rarely occurs.)
If MFT starting sector fails,
the whole $MFT would become unreadable
the pointer to the $MFTMirr would also be lost, so it's hard to determine what really does the $MFTMirr gain.
All instances of access to the objects on disk are considered series of transactions on NTFS. $LogFile records transaction progress.
Contains detailed info only about recent transactions -- it scrolls around in a circular fashion -- therefore, it's not the whole volume history.
Once the log is full, the first entry is overwritten with the next new entry.
Located at inode #2 of the $MFT
When a program is modifying a file, the following steps might occur:
read MFT entry for directory entry file is in
read directory entry file is in
read MFT record for file
write file
update A time in file's MFT record
update M time in file's MFT record
update A time in directory entry for that file
update M time in directory entry for that file
The list gets considerably longer if the file is encrypted or compressed.
If the program fails before all transaction steps are complete due to a crash, the system rolls back to the previous values in order to maintain consistency of the file system.
NOTE: This is not to be confused with running CHKDSK. NTFS itself is providing a reliable, crash-resilient environment.
Located at inode #3 of the $MFT
Contains
NTFS volume name
NTFS version number
Flags to signal operations to performed on boot:
run CHKDSK
upgrade to new version
resize the log file
contains VOLUME_INFORMATION attribute, which provides
major (1 or 3) and a minor version number of NTFS
flags:
Value Description
------ -------------------
0x0001 Dirty (chkdsk /f needs to be run on the next boot)
0x0002 Resize LogFile
0x0004 Upgrade on Mount
0x0008 Mounted on NT4
0x0010 Delete USN underway
0x0020 Repair Object Ids
0x8000 Modified by chkdsk
Located at inode #4 of the $MFT
Contains list of attributes availble on this version of NTFS.
For each attribute, the following info is provided:
Attribute name
ID
Usage rules (currently not in use)
Flags
0x02 = Indexed 0x40 = always Resident 0x80 = can be Non-resident
Max size
Min size
Min Max
Type Name Flags IRN Size Size
---- ---------------------- ----- --- ---- ----
0x10 $STANDARD_INFORMATION 0x40 R 0x30 0x48
0x20 $ATTRIBUTE_LIST 0x80 N
0x30 $FILE_NAME 0x42 IR 0x44 0x242
0x40 $OBJECT_ID 0x40 R 0x100
0x50 $SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR 0x80 N
0x60 $VOLUME_NAME 0x40 R 0x2 0x100
0x70 $VOLUME_INFORMATION 0x40 R 0xC 0xC
0x80 $DATA 0x00
0x90 $INDEX_ROOT 0x40 R
0xA0 $INDEX_ALLOCATION 0x80 N
0xB0 $BITMAP 0x80 N
0xC0 $REPARSE_POINT 0x80 N 0x4000
0xD0 $EA_INFORMATION 0x40 R 0x8 0x8
0xE0 $EA 0x00 0x10000
0xF0 $PROPERTY_SET
0x100 $LOGGED_UTILITY_STREAM 0x80 N 0x10000
0x40 = always Resident
0x80 = can be Non-resident
Located at inode #5 of the $MFT
Named "."
NTFS directories are stored in files
Directory attribute is set in the header
All attributes are assigned the name $I30
$MFT entry 5 points to Root Directory (named ".")
Root Directory points to subdirectories
Information is stored in a balanced tree structure
Balanced tree facilitates sorting, storing, and retrieval of information.
$INDEX_ROOT:
is a resident attribute of a directory entry
stores a single node with a small number of index entries.
Always the root of the index tree
$INDEX_ALLOCATION:
is a non-resident attribute of a directory entry (due to a potentially large index structure.)
Stores as many index records as required for directory
Each index record is usually 4,096 bytes in size
$Bitmap file describes the allocation status of each cluster in the file system
Entry #6 in $MFT
$DATA attribute in the file contains a string of bytes where each bit indicates whether the corresponding cluster is
available (0) or
allocated (1)
The size of $DATA is always a multiple of 8. Since each byte contains 8 bits, this is equivalent to saying that NTFS bitmap describes the disk in chunks of 64 clusters. However, in most cases the real size of a disk is not a multiple of 64 NTFS clusters. To avoid a mapping mismatch, there is usually a section at the end of the $Bitmap file that corresponds to the space beyond the end of the drive, and all bits of that section are always marked as 1.
The $DATA attribute is always non-resident.
$BITMAP attribute is used to describe the allocation status of index records and MFT entries.
The Defrag utility would want each byte in the bitmap to be either 0x00 or 0xFF. Anything else is "a hole" requiring a defragmentation.
Entry #7 in $MFT
Although appears as a regular file, the non-resident $DATA attribute points to the volume boot record (VBR), located in sector zero on NTFS volume.
Allows to bypass the file system to access the VBR without having to write special code and do the work via normal system API calls.
There is information in the VBR that certain utilities need, like BIOS parameter block, including
volume serial number, and
cluster numbers of $MFT and $MFTMirr.
$Boot is usually 8192 bytes long.
Entry #8 in $MFT
Tracks bad clusters in volume
Cluster is bad if at least one sector is bad
The $Bitmap marks bad clusters as 1-in use, preventing other files from trying to use the bad cluster in the future.
The $BadClus has the size of the NTFS volume:
Organized as a sparse file of all zeros
Zeros in sparse files are counted instead of saved
$BadClus takes no space on the disk: if a cluster becomes bad, the data is written into $BadClus instead at the same offset as if it was written on disk.
See also
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sparse_file
Entry #9 in $MFT
Contains
index for every file owner, $SII - Standard Information ID
index pointing to the Access Control List (ACL), $SDH Security Descriptor Hash
In Windows NT, every file had a $Security_Descriptor attribute storing this info. Since many files had the same values in this attribute, it was moved out to this file so that data wasn't repeated.
Entry #10 in $MFT
The size is 128 KB
Contains every uppercase character in UNICODE alphabet
Allows to compare and sort filenames without the need to switch to a particular Windows code page:
The case in the file name is always preserved, but the file name is converted to all UPPERCASE for sorting when the directory entry is created for the file.
Entry #11 in $MFT
This is a directory containing the various optional system files (aka extensions):
$ObjID
$Quota
$Reparse
$UsnJrnl
Although these four files could have all been given their own unique Inodes, $Extend spares them for other system files.
Located in $Extend directory
Contains index of each file that has an $Object_ID attribute
This allows files to be tracked by $Object_ID instead of the file name:
Most commonly used by Office documents, which can be linked and then the files can be renamed by the user without breaking the links of the compound Office file.
Located in $Extend directory (on Windows NT was inode #9)
Tracks how much space on the volume is allocated by every user.
Contains two indexes:
$O contains an entry for everyone that has a quota enforced on them.
$Q has an entry for every user login on the system.
When a file is accessed,
A lookup is done in $O for the file owner to see if they have a quota
A lookup is done in $Q to see what the quota is.
On NTFS the amount of space allowed for each user can be enforced at the file system level.
When a limit is set, it applies to all users on all volumes.
A warning level and a quota limit are set, the users are unpleasantly notified that they are above the warning level.
The users are "physically" prevented from writing to the volume if over the limit.
Quota is checked before NTFS compression is applied, so the limit is the logical size of the file -- not the amount of disk space it takes.
Support for disk quotas is not available in Basic, Home and Media Center versions of Windows.
Quotas must be activated after installation of Professional, Ultimate and Server versions of Windows.
Located in $Extend directory
Contains index for all reparse points on the volume
Allows to mount a portion of the file system as another volume
Reparse points are similar to Unix Mount Points

Directory on NTFS is actually a root of another volume
Allows a directory tree to replace multiple drive letters
Similar to multiple hard drives, CD/DVD ROM, and floppy drives as they appear as subdirectories on Unix as a single tree:
/dev/hda
/dev/hdb
/dev/cdrom
/dev/floppy
Those same four devices would be appearing as C:, D:, E:, A:, respectively, on Windows.
Located in $Extend directory
Similar to $LogFile, tracks changes that occur on files
Short-term repository:
some application requests to log the changes via system API
The application reads captured info
NTFS empties the $UsnJrnl file
Often called the Change Journal.
Useful for
file replication/mirroring applications
tracking of which files to include in an incremental backup
virus scanners
etc.
The file normally will appear empty: the data exists only while it is being used and goes away as soon as the program that needed it no longer does.
Deleted files are moved to the Recycle Bin in the RECYCLER directory
Files are renamed in the format Dx#.ext, where
x = lowercase drive letter from where the file was deleted
# = sequence number of the order in which the file was deleted
ext = original file extension
Every user who has deleted at least one file has an individual subdirectory, named with the user's SID
User's subdirectory contains desktop.ini, INFO2, and any files that this user has deleted.
INFO2 file:
keeps a lists of all files in the RECYCLER subdirectory.
stores the original path/file name.
contains ASCII data, Unicode data, and date/time of deletion for each deleted file or folder.
Once created, user's subdirectory is never deleted.
When a file is deleted at the command prompt,
The file does not go into the Recycle Bin.
Part of the file or the complete file can be recovered using forensic tools.
Tasks performed by the operating system (also when a file is permanently deleted from the Recycle Bin):
The clusters are made available for new data.
The MFT attribute $BITMAP is updated.
File attributes of the MFT are marked as available.
Any connections to the inodes and VFN/LCN cluster locations are removed.
The list of links to the cluster locations is deleted.
Alternate data streams (ADS) allow more than one data stream to be associated with a filename
The filename format is
filename:streamname
For example,
"text.txt:extrastream"
Alternate streams are not listed in Windows Explorer
The size of data in alternate streams is not included in the file's size.
Only the main stream of a file is preserved when it is copied to a FAT-formatted USB drive, attached to an e-mail, or uploaded to a website.
As a result, using alternate streams for critical data may cause problems.
NTFS data stream is a unique set of file attributes.
NTFS supports multiple data streams per file:
one main stream
plus an optional set of alternate data streams
A data stream can be created in an existing file on an NTFS volume using a command like
C:\>ECHO hello > myfile.txt:stream1
To display the contents of the data stream,
C:\>MORE < myfile.txt:stream1
A data stream does not appear when a file is opened in a text editor!
The only way to see if a data stream is attached to a file is by examining the MFT entry for the file.
An example of ADS usage by the applications is when a small ADS is added by the Internet Explorer and other Internet browsers to mark files that have been downloaded from the Internet.
Because downloaded content may be unsafe to run locally, the local OS shell will ask the user for a confirmation before opening downloaded files.
The user can open the properties dialog and drop the warning flag -- the result is that ADS attribute is simply removed from the MFT entry.
NTFS is capable of compressing
individual files
all files within a folder
all files/folders on the volume.
Compression is executed within NTFS.
Any Windows program can read/write compressed files without considering the extent of the compression.
When a compressed file is opened, only a part of the file is decompressed while being read.
Data already in memory is uncompressed.
Modified and new data is compressed again -- when written to the compressed file on disk.
NTFS compression algorithms support cluster sizes of up to 4 KB.
The best use of compression is for files which are repetitive, written seldom, usually accessed sequentially: log files are an ideal example.
Compresion works in blocks of 16 clusters
Data is compressed using a modified LZ77 algorithm, named LZNT1.
Each block is compressed independently
If compressed block does not become less than the original 16 clusters, it is left uncompressed.
Compressing a file adds serious complexity to the way the file is stored.
The MFT is the only place that contains information about what parts are compressed and by how much.
If MFT is corrupted there is little hope retrieving the data!
Reference:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LZ77
When NTFS encounters files with long runs of zeros, the system counts how many zeroes are present in the MFT header attribute. The counter is stored instead of actual data.
Long runs of zeros are common on disks, so counting them is an easy way to compress a file.
The counting mechanism kicks in when the run of zeros consumes an entire cluster.
The resulting "sparseness" of the file is annotated in the data run that maps the clusters allocated to the file.
To protect files from mishandling and to ensure their security, the files can be encrypted.
The Encrypting File System (EFS) is introduced in NTFS.
EFS uses symmetric key encryption technology with public key technology for encryption.
The user is supplied with a digital certificate with a public key pair.
A private key is not used for the users who are logged in to the local systems.
Instead, an EFS key is used for users who are logged in to the local system.
This encryption technology maintains a level of transparency to the user who encrypts the file.
See also
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Encrypting_File_System
Bootdisk-borne utility known as chntpw is a Linux utility to reset the password of any user that has a valid local account on a Windows system
Thus, chntpw allows a user with physical access to a system to change any user's (including the administrator's) password.
chntpw modifies encrypted password in the registry's SAM file.
chntpw does not need the knowledge of the old password to reset it.
chntpw works after booting from a linux floppy or CD disk, etc.
The bootdisk includes built-in access to NTFS partitions
However,
The normal Windows "change password" process updates the EFS encryption keys,
the chntpw backdoor method does not.
After chntpw, the user can log into the newly acquired account; but if NTFS drive is using EFS, the encrypted files remain encrypted and no automatic conversion to plaintext takes place.
chntpw boot menu example:

There is no need for users to decrypt the file when they access it to make changes.
After a user is done with the file, the encryption policy is automatically restored:
When any unauthorized user tries to access encrypted file, access is denied.
To enable the encryption and decryption facilities, a user has to set the encryption attributes of the desired files/folders.
All files/subfolders in an encrypted folder are automatically encrypted.
To take the best advantage of the encryption capability, experts recommend that encryption should be done at the folder level.
That means a particular encrypted file should not be kept in the same folder as other files that are not encrypted.
Encryption is done using the graphical user interface (GUI) in Windows, but a file or a folder can also be encrypted using a command line tool like Cipher.
A file encryption certificate is issued whenever a file is encrypted.
If the person who encrypted the file loses that certificate and the associated private key, data recovery is performed through the recovery key agent.
In case of a Windows 200X server-based network, which uses Active Directory, the recovery agent is assigned by default to the domain administrator.
The recovery agent holds a special certificate and related private key.
The recovery certificate is issued by a certification authority (CA).
Using the recovery certificate and its related private key, the agent can recover the data.
EFS uses symmetric key encryption (DESX with 128bit key) in conjunction with public key technology (RSA).
Users of EFS are issued a digital certificate with a public key and a private key pair.
This key pair is used to decrypt a File Encryption Key (FEK) file that holds the key to decrypting the data. Each encrypted file has an associated FEK encrypted with the public key of each user allowed to use the file.
With the FIPS-compliant algorithms usage turned on in LSA policy, the encryption is with 3DES using a 168-bit key. The process is completely transparent to the user.
Key management is handled by the Local Security Authority Subsystem, lsass.exe without the user's intervention.
The data is encrypted/decrypted as it passes to/from the drive. To turn EFS on, the user sets the encryption attribute in the file or folder's properties.
In addition to the individual user's public key information, each FEK also contains a recovery key. An entity, usually a domain administrator, is assigned as a Recovery Agent.
The recovery agent can decrypt ANY file, so an attacker who hijacks the recovery agent account has also hijacked the ability to read all encrypted data.
This requires that the user/administrator authenticate with the same password they normally do, so most attacks on privilege escalation render the data unrecoverable. There is an attack on the cached login credentials that an attacker can use.
Windows systems not on a network domain do not create a recovery agent.
References:
http://www.ntfs.com/ntfs-encrypted.htm
http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000/docs/encrypt.doc
http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000/techinfo/howitworks/security/encrypt.asp
Also known as Volume Snapshot Service or Volume Shadow Copy Service or VSS
The purpose is to provide an instant backup of files. Modified files are copied to the Shadow Copy of the volume on which the originals reside.
This NTFS feature is for backing up critical servers that can't afford the loss of data between traditional tape backups.
NTFS Shadow Copy can be accomplished in two different ways:
hardware-based, or
software-based.
The Shadow Copy can either operate in two modes:
Online backup mode:
functions like a RAID, where any transaction on one drive also happens on the other.
This is read/write, full copy mirror: both drives will have identical logical structure.
The clone drives are exact mirror images of the original.
Copy-on-write mode -- before file is modified on the original drive, the
"Original" + "Difference between new and unmodified copy"
is written to the shadow volume first. Then the modification of the file takes place on the original volume.
Copy-on-write mode operates like a mirror, but provides that any modification has a "prior version". This allows for the original drive to be rolled back in case if a write transaction goes bad. Thus,
Shadow Copy = Original + Difference
Copy-on-write can be much faster than the online backup, because only the changes are written instead of everything. (The original must still be available to maintain the shadow copy, but is written just once.)
NOTE: Unlike a true versioning file system, the users cannot trigger creation of new versions of an individual file -- only the entire volume.
Reference:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shadow_Copy
Windows Server
(technet.microsoft.com)
Other names:
Volume Snapshot Service
Previous Versions
Shadow Copies for Shared Folders
VSS
Beginning with Windows Vista, and continued by Windows 7, the VSS is used by the System Protection component.
System Protection creates and maintains periodic copies of system and user data on the same local volume.
(This is similar to the Shadow Copies for Shared Folders feature in Windows Server)
System Protection allows is used by System Restore.
The System Restore allows reverting to an entire previous set of shadow copies called a Restore point.
A shell extension called Previous Versions allows restoring individual files and entire folders locally from the existing restore points, retrieving an earlier version of a file or recovering a file deleted by mistake.
The shadow copy is not created every time a file is changed. The backup copy (a restore point) is created
automatically once per day, or
manually when running the backup utility, or
manually when the installer program is run on the system.
Previous Versions shell extension comes with
Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista, and
all Windows 7 editions.
The Volume Snapshot Service is included and running on all editions of Vista, including the Home Editions:
Using third party tools it is still possible to restore previous versions of files on the local Vista or Windows 7 volume.
On Windows Vista and 7, by turning off system restore all previous restore points are deleted.
Locate "my computer" icon, right click and choose properties.
The "Control Panel\System" dialog box appears.
Click "System Protection" link
UAC warning appears
Click the "System Protection" tab (sometimes may appear named "System Restore" tab):
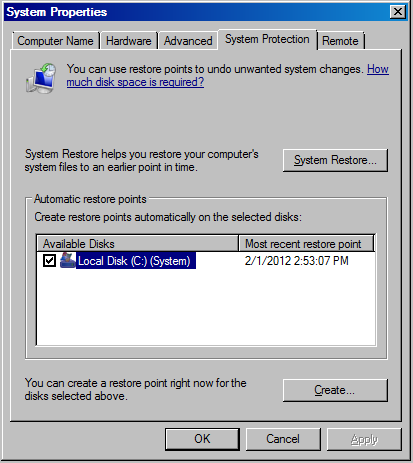
Click "System Restore" button to examine the history of existing restore points. Typically there are 15 of them or so.
Trying uncheck the volume on the list triggers the warning:
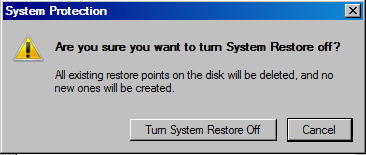
Clicking the button "Turn System Restore Off" will delete the existing restore points.
Click apply, then click OK. Done.
Abbreviated as SIS
If several directories contain same exact file, only one instance will really exist.
Two-part function:
NTFS "filter" that manages the copies
User space service Groveler searches for identical files to merge
Again, this feature is designed for servers containing multiple installation programs in which many of the files could be the same coming from different distributions of software install packages.
If SIS is disabled after it has been running, only the Groveler is disabled.
The SIS file system "filter" component must remain active as long as there are merged files on the volume.
There will be a SIS Common Store folder that contains information about which files are linked. If this folder is deleted, all of the linked files will become inaccessible.
Reference:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;299726