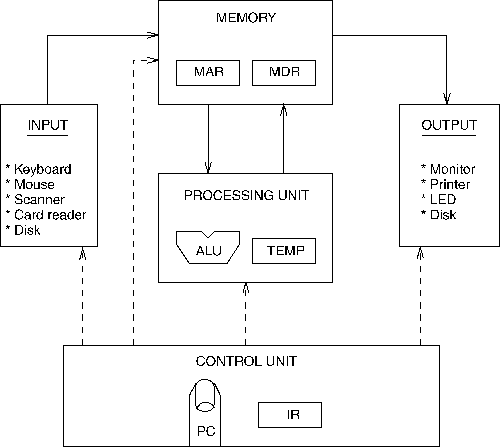
-
The CPU has a set of built-in operations (its instruction set) that is far richer than with the Turing machine, including the arithmetic, logic, interrupt facilities, and memory access:
-
devices: , , , , , , , and so on.
-
ability to branch to another part of a program, if the binary integer in some register is equal to zero (conditional branch),
-
stack operations, etc.
-
-
The CPU can interpret the contents of memory either as instructions or as data according to the fetch-execute cycle.
-
The von Neumann Machine: