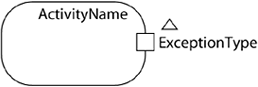
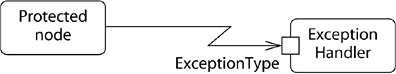
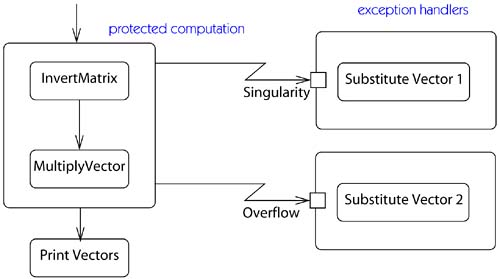
-
Method overloading means that the same method name is used over and over again,
but method signature is different every time. -
Method signature consists method name and a parameter list.
-
Method signature does not include the return type.
-
Java method signature components are as follows: